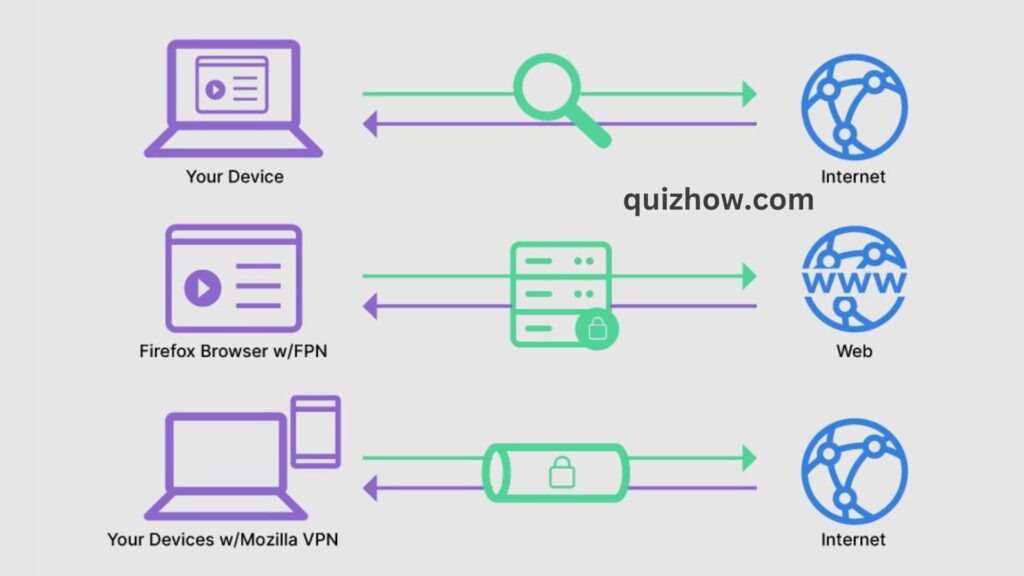
While both proxies and VPNs offer privacy, they work in different ways. A proxy simply acts as a middleman between you and the internet, whereas a VPN goes further by routing your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel, providing an extra layer of security. This makes VPNs a more secure option for protecting your network.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server acts as a bridge between you and the internet, often called an intermediary server because it sits between you and the websites you visit. Since a proxy server has its own IP address, your online activities appear to be coming from a different location. It can also be configured like a firewall or web filter to protect your devices from cyber threats.
There are several types of proxy servers, including:
Forward Proxy
A forward proxy sits in front of users and helps them access data on the internet, especially for groups within a private network. When you send a request, the proxy checks it to decide whether to connect. It’s great for networks that need a single entry point, offering security for IP addresses and easy management. However, it might limit how well it meets the needs of individual users.
Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy lets you browse the internet just like you would at home, making it “transparent.” Sometimes, users are connected to these proxies without even knowing it. They’re perfect for companies that want to use a proxy without employees realizing it. The benefit is a smooth, seamless experience. But, they’re more vulnerable to certain security threats, like SYN-flood denial-of-service attacks.
Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy hides your identity when you’re online, making your activities untraceable. It’s ideal for users who want complete privacy. While it offers excellent protection, using one can sometimes be seen as sneaky, and it might lead to pushback or discrimination.
High Anonymity Proxy
A high anonymity proxy goes a step further by erasing your information before connecting to a website. This is best for those who need total privacy, like employees who don’t want their activities tracked. However, some free versions might be traps to steal your personal information.
Distorting Proxy
A distorting proxy tells websites it’s a proxy but hides its actual identity by changing its IP address. It’s a good choice for people who want to hide their location. This proxy can make it look like you’re browsing from a different country, protecting both your identity and the proxy’s. But, some websites might block distorting proxies, preventing you from accessing certain sites.
Data Center Proxy
Data center proxies aren’t linked to an internet service provider (ISP); instead, they come from another company’s data center. These proxies offer quick response times and are affordable, making them great for people who need to gather information fast. However, they don’t provide the highest level of anonymity, which could put your identity at risk.
Residential Proxy
A residential proxy gives you an IP address tied to a real, physical device. All your internet requests go through that device. These proxies are great for verifying ads on your site, helping block unwanted or suspicious ads. While they are more reliable than other proxies, they tend to be more expensive, so it’s important to weigh the costs and benefits.
Public Proxy
A public proxy is free and open for anyone to use. It hides your identity by letting you use its IP address when browsing. Public proxies are best for those who prioritize cost over speed and security. But, they’re often slow due to heavy traffic and can increase the risk of your information being accessed by others online.
Shared Proxy
Shared proxies are used by multiple people at the same time. They provide an IP address that’s shared among users, allowing you to browse the internet as if you’re in a different location. They’re a budget-friendly option but can be slow. Plus, if someone else misuses the proxy, you could end up banned from certain sites.
SSL Proxy
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) proxy provides encryption between your device and the server, keeping your data secure and hiding the proxy’s existence. It’s great for organizations needing extra protection against threats that SSL can detect and block. Plus, since Google favors SSL, using this proxy with your website might boost its search ranking. The downside is that content encrypted with SSL can’t be cached, which might slow down your browsing experience.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN is like a proxy server because it makes your internet traffic look like it’s coming from a different location. But, unlike a proxy, a VPN encrypts your data, sending it through a secure tunnel between your device and the VPN network. This makes VPNs a great choice for keeping your online activities private and secure.
Using a VPN from a trustworthy provider is especially important when you’re browsing on public Wi-Fi, like in a café. Instead of connecting directly to the local Wi-Fi, which might have weak security and could expose your private information, you connect to a VPN, ensuring your data stays safe.
There are different types of VPNs:
Corporate VPN
Businesses use corporate VPNs to protect their employees’ devices and data, no matter where they’re connecting from.
Individual VPN
These are VPN services designed for personal use, giving individuals a secure way to browse the internet.

Proxy vs VPN
At first glance, VPNs and proxy servers might seem alike, but there are important differences to keep in mind. When choosing between a proxy server and a VPN, businesses should think about:
Security
Proxy servers can hide your identity from websites, but they don’t encrypt your connection. This means using a public proxy server is less secure than connecting directly through a browser. On the other hand, VPNs offer stronger security by encrypting your data before sending it, so your identity stays hidden from both the web and your internet service provider (ISP).
Privacy
Both VPNs and proxy servers hide your IP address, but they handle your data differently. Proxy servers act as a “middleman” between you and the web, hiding your IP address from the sites you visit. However, they don’t secure the data being sent and received.
A VPN goes a step further by not only hiding your IP address and location but also using end-to-end encryption. This means your ISP or router can’t access your data, giving you total privacy. Even if someone intercepts your encrypted data, they won’t be able to use it without decrypting it first.
Speed
A proxy is a single server that many people might use at the same time, which can slow down your connection. Free proxies tend to be even slower. VPN servers that are far from your location can also cause a slight delay, but if you choose a good VPN provider with up-to-date technology, any slowdown should be barely noticeable.
Also Read: Best 18 Task Automation Tools for 2024
How Fortinet Can Help?
In today’s fast-changing world of cybersecurity, relying on a VPN alone might not be enough to protect sensitive data and keep your organization’s network secure. Whether your team is in the office, working from home, or on the go, they need secure and reliable access to cloud applications, data centers, and SaaS platforms.
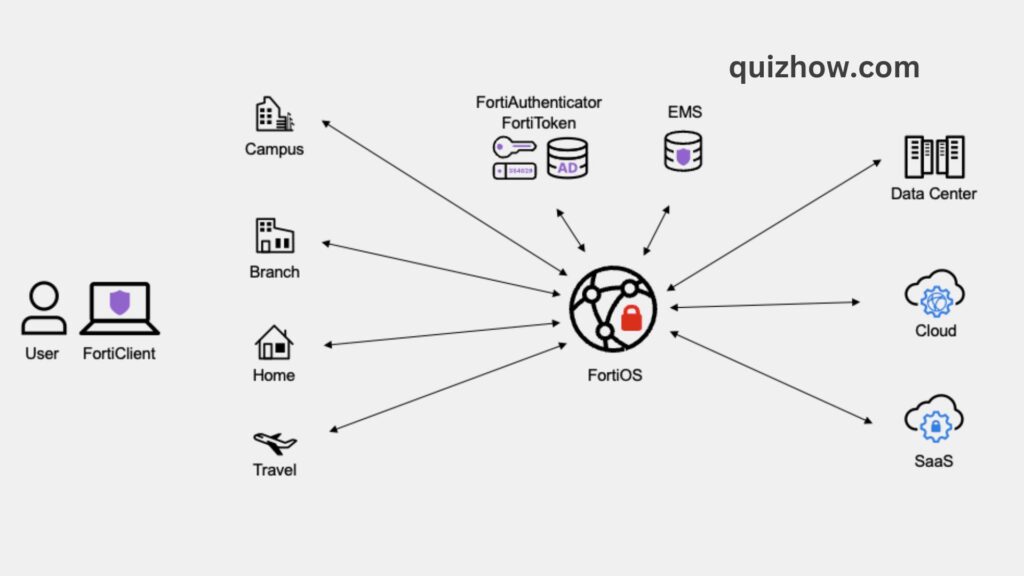
Fortinet helps organizations connect and protect their work-from-anywhere employees and devices. Fortinet Universal ZTNA is a powerful security solution that offers businesses flexibility, detailed access control, and continuous verification. It enforces security policies for users no matter where they are. With its granular access control, users can only access specific applications for the duration of their session, enhancing security. The client-initiated model gives the IT team more visibility and control over devices while providing users with a faster, simpler experience. Plus, Universal ZTNA is included for free in FortiOS and FortiClient, so you can switch from VPN to ZTNA at your own pace. Fortinet’s flexibility means you don’t have to choose between VPN or ZTNA—you can use what works best for your needs.
As users move between office, home, and public networks, it’s essential to have a unified security framework that connects zero trust, endpoint, and network security. Fortinet’s solutions, unified by a common set of APIs and integration points, ensure that users can smoothly transition between different locations while maintaining a consistent, secure experience. Fortinet is the only vendor that offers this integrated approach, providing proactive, context-aware security that automatically adapts to where users are, what device they’re using, and what resources they’re accessing.
With Fortinet’s broad range of zero trust, endpoint, and network security solutions within the Fortinet Security Fabric, you get security, services, and threat intelligence that follow users across different networks. The Security Fabric adjusts its protection based on the perceived risk of each interaction, whether your team is on the road, at home, or in the office, ensuring consistent enterprise-level security and enhanced productivity.

Discover more from QuizHow
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


1 thought on “Proxy vs VPN: Key Differences”